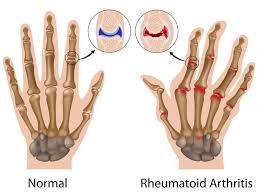
Bones provides support for the body and aids it in its movement, the place where two or more bones meet is called the joint. Joint may be immoveable slightly moveable or freely moveable. The synovium membrane surrounds the moveable joints inside the membrane the synovia fluid lubricates and flourishes the joint tissue such as cartilage. Articular cartilage is a tough slippery white tissue covering on ends of the bone, which allows smooth joint movement. Joint gives the body flexibility position of movement and help in support the body’s weight.
Arthritis is any disorder that affects the joints it causes pain and inflammation. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease this means the body attacks itself by mistake and the patient lives with chronic pain. The pain that can happen in Rheumatoid Arthritis can affect multiple joints in the body. The joint most commonly affected are the hands wrists and its usually symmetry. By symmetry it typically occurs at the same joint by both side of the body. It can affect both hands and wrists, and can also affect other joints of the body in areas such as knee ankle feet’s hips elbow shoulders and in neck. In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks joints and organ tissues.
How the immune system attack itself
The White Blood Cell (WBC) move into the joint, they release chemicals called cytokines which attack the cell of the synovium membrane. These chemicals cause synovium cells to release other destructive substances, they also cause the synovium membrane to grow new blood vessels and form a thickened area called a pannus overtime, as the pannus grows, it invades and destroys area of cartilage and bone inside the joint. Inflammation causes fluid build-up in the joints making the joint swell; eventually, without treatment, the joints space narrows and Ankylosis can occur. Ankylosis is the growing together of bones in the joint which result in the loss of ability to move the joint. There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis.
Warning Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Fatigue
- Loss of function
The stiffness is infrequently worse in the morning when patients will describe waking up and needing extra time to get ready for their day and the stiffness can last from 30min to two hour. Usually stiffness will get better with moving around or a hot shower will help with stiffness. Swelling can be seen in the hands and in the wrists. The joints can become really enlarged and fluid can be present in the joints. You can also see fluids in the knee and ankle.
The fatigue that some patient with RA can experience can be overwhelming which may be a reason to visit their physicians. The fatigue can last all day, it can be difficult in sleeping or having to sleep all the time. It can occur for different reasons. It can be secondary to pain or stiffness to joint or because of fatigue they may not exercise. When patient experience these difficulties, they need to be seen by their physicians and referred to a rheumatologist.
What to control and manage in Arthritis Disease
- Weight and doing exercise
- Depression (by not wanting to do more)
- Unhappiness
- Stiffness in the morning
- Feeling shattered
- Movement of pain from joint to joint
1 in 5 patients will be depressed in an early phase of arthritis the pain may get people down. If the symptoms of depression are the response to the illness, then we help people to manage their illness and their symptoms of depression will leave. It is vital to help people deal well with the emotional aspect, it is very important to look at the whole passion of rheumatoid arthritis, not just the swelling joint but the emotional side of the condition and their functionality. What bothers patients the most are the fatigue and the drugs they have never used before. The important thing is discussing the drugs with them, they need to understand the drug an follow-up their regular blood monitoring. These will improve the outcome of the quality of life, the lower the joint damage the life expectancy will increase for at least five years. Modern treatment hasn’t shown so much of joint damage or deterioration apart from an elderly patient who has had Arthritis for a long time. This is because, newer drugs are setting off greater promise. The clinicians need to put the disease into remission.
References
Arthritis UK
British Society for Rheumatology (BSR)

